Bearing lock nuts / Sexagonal version

- Promotional pricing
- Volume Discount
- Stock
Part Number
Once your search is narrowed to one product,
the corresponding part number is displayed here.
- Drawing / Specifications
- 3D Preview 3D preview is available after complete configuration
- Part Numbers
- More Information
- Catalog
Back to the Category Groove Nuts/Shaft Nuts
Technical drawing - Locknuts
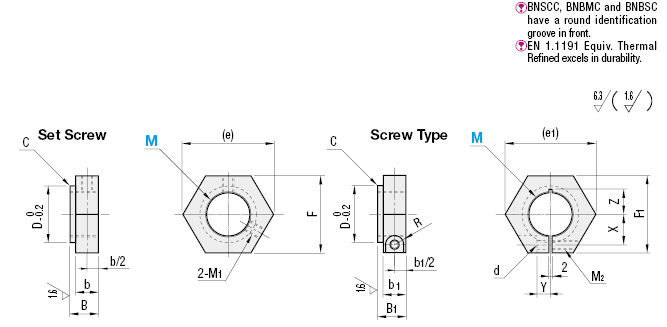
Open the technical drawing in the new window
Available dimensions and tolerances can be found under the tab More information.
Basic properties (e.g., material, hardness, coating, tolerance) - Locknuts
| Type | Coarse | Fine | Material | Hardness | Surface Treatment | Accessory | |
| Set Screw Type | BNCM | BNSC | EN 1.0038 Equiv. | - | Black Oxide | Set Piece (Copper Alloy) | Set Screw (EN 1.7220 Equiv.) |
| - | BNSCC | EN 1.1191 Equiv. Thermal Refined | 20~24HRC | ||||
| BNCMS | BNSCS | EN 1.4305 Equiv. | - | - | Set Screw (EN 1.4301 Equiv.) | ||
| Screw Type | BNBM | BNBS | EN 1.0038 Equiv. | - | Black Oxide | Hex Socket Screw (EN 1.7220 Equiv.) | |
| - | BNBSC | EN 1.1191 Equiv. Thermal Refined | 20~24HRC | ||||
| BNBMS | BNBSS | EN 1.4305 Equiv. | - | - | Hex Socket Screw (EN 1.4301 Equiv.) | ||
Composition of a product code - Locknuts
|
General Information - Locknuts

Selection Details of - groove nut/shaft nut
- Material: stainless steel, steel
- Coatings: burnished, phosphate conversion coating
- Thread diameter (metric): M3 to M60
- Thread diameter (in inches): 0.391” to 12.562”
- Thread pitch (metric): fine thread, control thread
- Locking method: with adjusting screw, with clamping screw, with locking plate
- Drive form: grooves, hexagon, square
Description/Basics - groove nut/shaft nut
Groove nuts and shaft nuts are used to secure ball bearings and roller bearings to a shaft.
Using a shaft nut, a ball bearing can be clamped against a shoulder, for example on a rotary shaft. The inner ring of the bearing is thus firmly positioned on the shaft pin and the bearing is fully secured against axial displacement.
MISUMI offers various drive forms for shaft locknuts. The hexagon socket, which is the most common drive form for nuts in general, is also available for shaft nuts. This allows the locknut to be tightened and loosened without a complicated special tool.
The bearing lock nut with external hexagon can be secured by using either a set screw, a clamping set screw or a bearing lock nut. In the case of the locking plate, there must be a keyway in the shaft or in the shoulder of the shaft. The keyway ensures that the inner tab of the locking plate can lock into it. The outer tabs are turned over after tightening the shaft nut and thus secure the nut against loosening and at the same time against improper tightening.
In addition, there is also a bearing nut in square form. The anti-rotation lock is optionally done via an adjusting screw or a locking plate. The square serves as a drive and has a common wrench width.
In contrast to a shaft nut with a hexagon or square drive, a hook wrench was required to tighten nuts. The articles MISUMI offers are similar to those of DIN 981 for groove nuts and DIN 1810 for spanner wrenches.
The key is inserted with the hooks into the grooves of the shaft nut and moved clockwise or in the opposite direction. The lever rotates the thread of the nut on the thread of the shaft pin and the nut clamps or secures the bearing.
The size of the hook wrench is not based as usual on the width of a conventional nut. The underlying value here is the shaft diameter suitable for the nut (shaft Ø, see Table), which is referred to as number (for no., see Table) at MISUMI.
Thus, the hook wrench with the article number MFK16 is suitable for the shaft diameter 16 mm and 18 mm, which corresponds to a thread diameter of M8 or M10 respectively.
Another type of locking is the self-locking bearing nut. This variant of a bearing lock nut is a two-part nut. One half of the nut has an outer cone that fits into the inner cone of the second half. If the two halves of the nut are tensioned against each other, friction develops in the area of the cone, which inhibits self-loosening. This type of shaft nut is also driven by a hook wrench.
This type of bearing locking does not need a keyway compared to the locking plate, with the same number of assembly parts. As a result, the design requires less effort, which in turn reduces development costs and production costs.
Application Examples - Locknuts
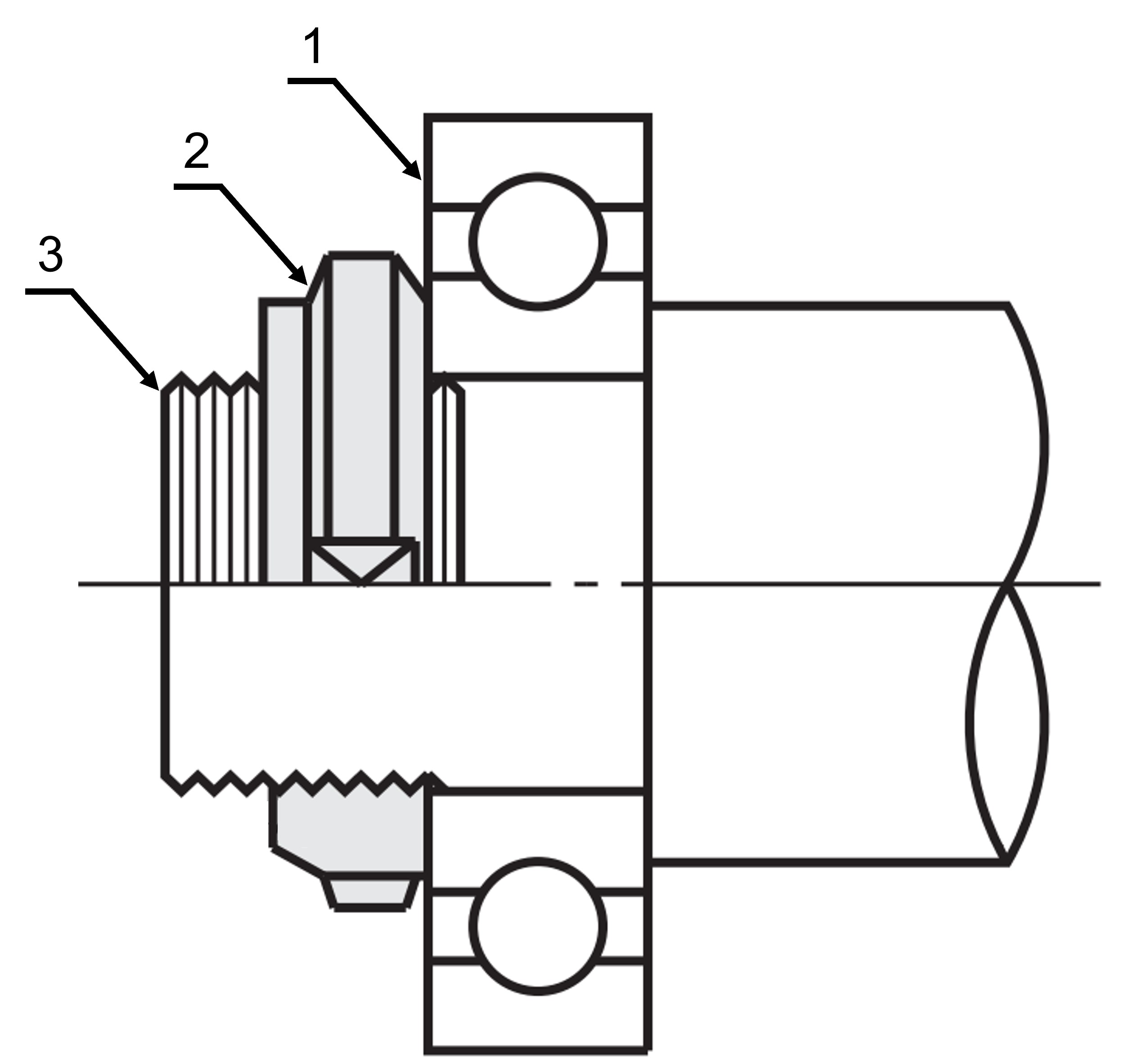
Application example: groove nut
(1) Ball bearing, (2) Shaft nut, (3) Rotary shaft

Application example: self-locking shaft nut
(1) Upper part shaft nut, (2) Lower part shaft nut, (3) Rotary shaft
Industrial applications




Part Number:
- In order to open the 3D preview, the part number must be fixed.
3D preview is not available, because the part number has not yet been determined.
Part Number
|
|---|
| BNBM20 |
| BNBMS20 |
| BNCM20 |
| BNCMS20 |
| Part Number |
Standard Unit Price
| Minimum order quantity | Volume Discount | RoHS | Thread Nominal M | Material | Surface Treatment | Screw Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
20.07 € | 1 | Available | 5 Days | 10 | M20x2.5 | [Steel] Steel | Surface Treatment Provided | Metric (Coarse) Thread | |
31.28 € | 1 | Available | 5 Days | 10 | M20x2.5 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Surface Treatment | Metric (Coarse) Thread | |
13.39 € | 1 | Available | 5 Days | 10 | M20x2.5 | [Steel] Steel | Surface Treatment Provided | Metric (Coarse) Thread | |
20.81 € | 1 | Available | 5 Days | 10 | M20x2.5 | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | No Surface Treatment | Metric (Coarse) Thread |
Loading...
Back to the Category Groove Nuts/Shaft Nuts
Technical drawing - Locknuts

Open the technical drawing in the new window
Available dimensions and tolerances can be found under the tab More information.
Specification Tables - Locknuts
| Part Number | MxPitch | D | C | Set Screw | Screw Type | Unit Price | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BNCM | BNSCC | BNCMS | BNBM | BNBSC | BNBMS | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Type | M | Coarse | Fine | (e) | F | B | b | M1 | (e1) | F1 | B1 | b1 | M2 | X | Y | Z | d | R | BNSC | BNSCS | BNBS | BNBSS | |||||
| (Coarse Set Screw) BNCM BNCMS (Coarse Screw) BNBM BNBMS (Fine Set Screw) BNSC BNSCC BNSCS (Fine Screw) BNBS BNBSC BNBSS | *5 | M5x0.8 | M5x0.5 | 9 | 0.2 | 19.6 | 17 | 9 | 5 | M3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| *6 | M6x1.0 | M6x0.75 | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | M8x1.25 | M8x1.0 | 13 | 21.9 | 19 | 27.7 | 24 | 13 | 9 | M4 | 7 | 4 | 7 | (8.5) | 4.5 | 3.75 | |||||||||||
| 10 | M10x1.5 | M10x1.0 | 16 | 25.4 | 22 | 10 | 6 | M4 | 31.2 | 27 | 9 | 7 | (10) | ||||||||||||||
| 12 | M12x1.75 | M12x1.0 | 17 | 27.7 | 24 | 34.6 | 30 | 16 | 12 | M5 | 9.5 | 4.5 | 9 | (11) | 5.5 | 4.5 | |||||||||||
| 15 | - | M15x1.0 | 21 | 31.2 | 27 | 11 | 41.6 | 36 | 19 | 14 | M6 | 12.5 | 5 | 9.5 | (11) | 7 | 5.5 | ||||||||||
| 16 | M16x2.0 | - | 9.5 | (12) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20 | M20x2.5 | M20x1.0 | 26 | 37.0 | 32 | 47.3 | 41 | 15 | 6.5 | 12 | (15) | ||||||||||||||||
| 24 | M24x3.0 | - | 33 | 47.3 | 41 | 13 | 8 | M5 | 53.1 | 46 | 17 | 7.5 | 15 | ||||||||||||||
| 25 | - | M25x1.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30 | M30x3.5 | M30x1.5 | 39 | 0.5 | 57.7 | 50 | 16 | 10 | M6 | 57.7 | 50 | 20 | 19.5 | 8.5 | 18 | ||||||||||||
| * End Face M5 and M6 are available for Set Screw only. Z dimensions in ( ) are for Stainless Steel Type. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Basic information
| Type | Lock Nuts | Shape | Hex |
|---|
Configure
Basic Attributes
-
Material
- Steel
- EN 1.4301 Equiv.
- Steel
-
Surface Treatment
- Surface Treatment Provided
- No Surface Treatment
-
Screw Type
- Metric (Coarse) Thread
- Metric (Fine) Thread
-
Type
- BNBM
- BNBMS
- BNBS
- BNBSC
- BNBSS
- BNCM
- BNCMS
- BNSC
- BNSCC
- BNSCS
-
Thread Nominal M
-
Filter by CAD data type
- 2D
- 3D
Filter by standard shipping days
-
- All
- Same day
- 5 Days or Less
Optional Attributes
- The specifications and dimensions of some parts may not be fully covered. For exact details, refer to manufacturer catalogs .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Question:
Do I need a special tool for installing a nut?
-
Answer:
A hook spanner is required to install the nut. It is inserted with the hook into the groove of the shaft nut and thus prevents damage when tightening.
-
Question:
Is the size of the locknut wrenches comparable to that of wrenches?
-
Answer:
The size of the hook wrenches is specified in numbers (no.) at MISUMI. The information refers to the diameter of the shaft. One number always covers two shaft diameters. For details, see the Table below of this PDF.
-
Question:
How can I secure the shaft nut against twisting on the shaft with a keyway?
-
Answer:
A bearing lock nut can be secured to a shaft by means of a locking plate. However, a shaft with a keyway is more costly than a shaft without.
-
Question:
Is there a way to secure the shaft nut to the shaft without a keyway?
-
Answer:
With the help of a self-locking locknut, the bearing can also be secured without a keyway. Alternatively, a nut with adjusting screw can be used.
Complementary Products
MISUMI Unit еxample related to this product
Tech Support
- Technical Support
- Tel:+49 69 668173-0 / FAX:+49 69 668173-360
- Technical Inquiry