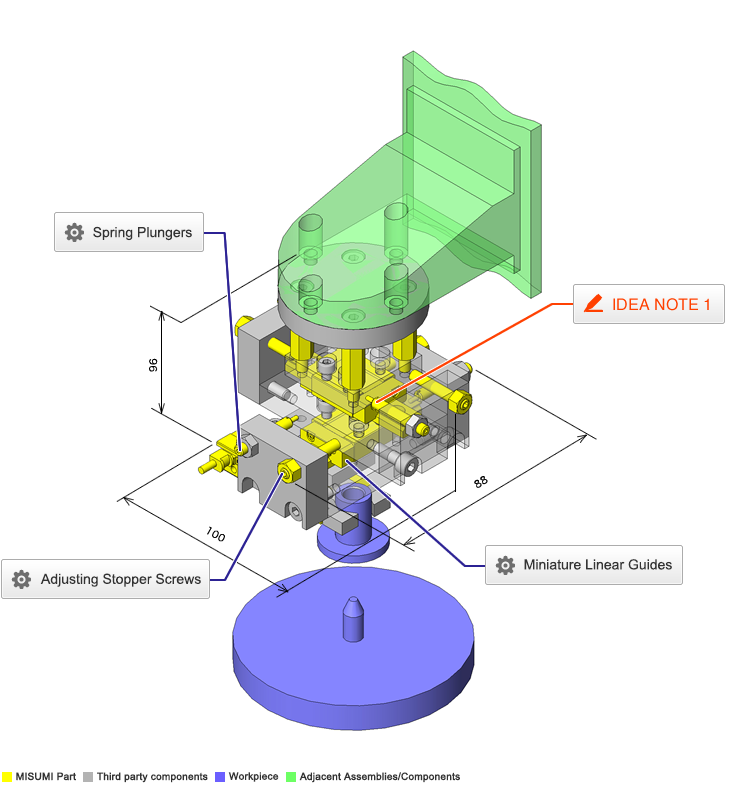
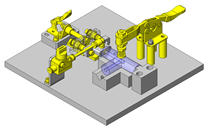
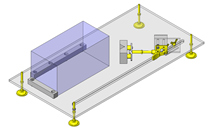
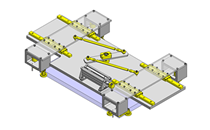
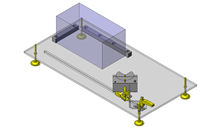
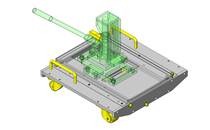
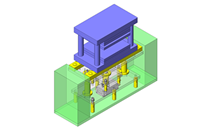
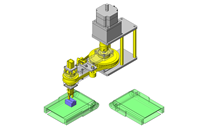
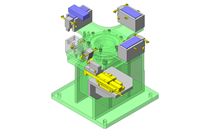
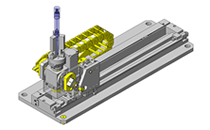
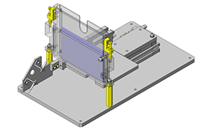
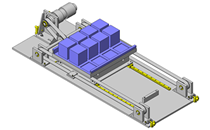
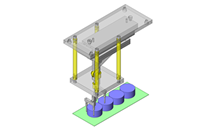
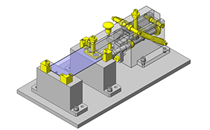
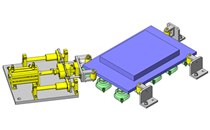
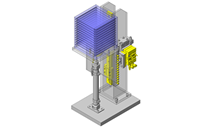
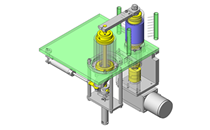
Miniature Linear Guides
| Product name | Miniature Linear Guides/Standard Blocks/Light Preload |
| Part number | SEB10-55 |
| Features | The most basic type among all the industry standard-compliant blocks. |
* Orange colored cells in the table below indicate the part numbers used in this example.
Selection criteria
Effective when linear motions are needed in limited space
Back to page top
Available sizes
■Miniature Linear Guides (standard blocks, light preloading, slight clearance)
| Material | Hardness |
| Stainless steel | 56HRC ~ |
|
|
|
|
Carbon steel
Carbon Steel (Alloy Steel including SCM) | 58HRC ~ |
|
|
|
|
■Sizes and Dimensions
| Number of Blocks | Block Width | Block Length | Overall Height | Rail Length |
| 1 | 12 | 17.4 | 6 | 25 - 100 |
| 17 | 23.6 | 8 | 40 - 130 |
| 20 | 30 | 10 | 35 - 275 |
| 27 | 33.9 | 13 | 45 - 470 |
| 32 | 42.4 | 16 | 70 - 670 |
| 40 | 50 | 20 | 100 - 700 |
| 2 | 12 | 17.4 x 2pcs. | 6 | 70 - 100 |
| 17 | 23.6 x 2pcs. | 8 | 70 - 130 |
| 20 | 30 x 2pcs. | 10 | 75 - 275 |
| 27 | 33.9 x 2pcs. | 13 | 95 - 470 |
| 32 | 42.4 x 2pcs. | 16 | 110 - 670 |
| 40 | 50 x 2pcs. | 20 | 160 - 700 |
Back to page top
Selection Steps
- Determination on Operating Conditions
- (Moving mass, feed rate, motion pattern, life)
↓
- Temporary selection of linear guide specifications
- (Number of blocks, block type, height and rail length are temporarily selected based on the usage conditions.)
↓
- Basic safety check
-
- ●Allowable Load
- ●Operating Life
- ●Preload
Back to page top
Accuracy Info
■Preload and Accuracy Standards (standard blocks, light preload, slight clearance)
(µm)
| Specification | Light Preload,
High Grade | Light Preload,
Precision Grade | Slight Clearance,
Standard Grade |
|
| Radial Clearance | - 3 - 0 | 0 ~ +15 |
| H Dimension Tolerance | ±20 | ±10 | ±20 |
| Pair variation of H | 15 | 7 | 40 |
| Tolerance of dims. W2 | ±25 | ±15 | ±25 |
| Pair variation of W2 | 20 | 10 | 40 |
■Running Parallelism
(µm)
| Rail length (mm) |
| - 80 | 81 - 200 | 201 - 250 | 251 - 315 | 316 - 400 | 401 - 500 | 501 - 630 | 631 - 700 |
| Precision Grade | 2 | 3 | 3.5 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 6 |
| High Grade | 3 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 11 | 12 | 13.5 | 14 |
| Standard Grade | 13 | 15 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 19 | 21 | 21.5 |
* The slight clearance type has clearances (play) between the rail and blocks.
Back to page top
Performance info.
Rated Load of Linear Guide (wide standard blocks, slight clearance)
| Overall Height | Basic Load Rating | Allowable Static Moment |
| C (Dynamic) kN | Co (Static) kN | MA
N・m | MB
N・m | Mc
N・m |
| 6 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 1.5 |
| 8 | 0.9 | 1.5 | 4.1 | 4.1 | 5.2 |
| 10 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 5.1 | 4.1 | 10.2 |
| 13 | 2.2 | 3.3 | 8.8 | 9.5 | 16.1 |
| 16 | 3.6 | 5.4 | 21.6 | 23.4 | 39.6 |
| 20 | 5.2 | 8.5 | 48.4 | 48.4 | 86.4 |
Back to page top
Technical Calculations
■Linear guide life calculations
- ●Life
- When linear guides operate in linear motion while supporting loads, repeated stresses apply on the rolling elements (balls) and raceways (rails), eventually causing scale-like flaking due to material fatigue. The total run distance until this flaking appears is defined as linear guide's "Life".
- ●Rated Life
- Rated life is a total distance 90% of linear guides reach without flaking when a group of the same guides are run under the same condition. The rated life can be calculated with basic dynamic load rating and the load applied on the guides as follows.
-

- When using linear guides, load calculations are initially needed. It is not easy to calculate the loads during linear motion due to vibrations and shocks, as well as load distribution on the guides. Furthermore, operating environment temperature has large effect on life. When these conditions are taken in consideration, the calculations would be as follows.
-

- L: Rated Life (Km)
- fH: Hardness Factor (See Fig.1)
- fT: Temperature Factor (See Fig.2)
- fC: Contact Factor (See Table-1)
- fW: Load Factor (See Table-2)
- C: Basic Dynamic Load Rating (N)
- P: Applied Load (N)
- ●Hardness factor (fH)
-

In using linear guides, the shaft that balls contact must have sufficient hardness, If adequate hardness cannot be obtained, load rating decreases and life will be reduced as a result.
Please correct the rated life with the hardness factor.
- ●Temperature Factor (fT)
-

When the temperature of linear guides exceed 100°C, hardness of blocks and rails will be reduced, causing reduction of life. Please compensate the life rating with temperature factor.
* Please use linear guides within temperature shown on product pages.
- ●Contact Factor (fC)
-
Table-1. Contact Factor
Number of Blocks per Rail Contact Factor fC
| 1 | 1.00 |
| 2 | 0.81 |
| 3 | 0.72 |
| 4 | 0.66 |
| 5 | 0.61 |
In general, it is common to use 2 or more blocks on 1 rail. In such case, load applicable on each block would not be uniform due to machining variations. As the result, allowable load rating on each block would vary depending on the number of blocks used per rail. Please compensate the life rating with contact factor shown on Table-1.
- ●Load Factor (fW)
-
Table-2. Load factor
| Application condition | fw |
No external shocks or vibrations and
speed is low 15m/min or less | 1.0 - 1.5 |
No significant shocks or vibration and
med. speed 60m/min or less | 1.5 - 20 |
External shocks and vibrations exist
and the speed is high 60m/min or over | 2.0 - 3.5 |
When calculating loads applicable on linear guides, other than the weight of the object, inertial force due to motion speeds, moment loads, and variations of each over time must also be obtained accurately. However, accurate calculation would be difficult due to repeated starts and stops and various shocks and vibrations. Therefore, the Load Factors shown in Table-2 are used to simplify the life calculations.
- ●Applied Load P Calculation Method
- When moment loads apply a block, use the following formula to convert the moment load to applicable load.
-

- P: Applied Load (N)
- F: Downward load (N)
- Co: Static load rating (N)
- MA: Allowable Static Moment - Pitching Direction (N・m)
- MC: Allowable Static Moment - Rolling Direction (N・m)
- Lp: Load Point Distance (m) in Pitching Direction
- Lr: Load Point Distance (m) in Rolling Direction
Back to page top
Spring Plungers
| Product name | Spring Plungers/Stainless Steel |
| Part number | PJXW4-4 |
* Orange colored cells in the table below indicate the part numbers used in this example.
Selection criteria
Effective as space saving and low price components for positioning reaction force
Back to page top
Available sizes
■Spring Plungers - Stainless Steel
Nose
Material | Load Type | Body | Pin | Spring | Operating Temperature |
| Material | Material | Hardness | Material |
| Stainless Steel | Ultra Light Load | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | EN 1.4125 Equiv. | 55HRC ~ | EN 1.4568 Equiv. | -30 ~ 260°C |
| Light Load |
| Heavy Load |
| Extra Heavy Load |
| Plastic | Ultra Light Load | Polyacetal | - | -30 ~ 80°C |
| Light Load |
| Heavy Load |
| Extra Heavy Load |
■Sizes and Dimensions
Screw Dia.
(Coarse) | Nose | Body length |
| Diameter | Stroke |
| M3 | Ø1 | 1.5 | 15 |
| 3 | 15 |
| M4 | Ø1.6 | 2 | 15 |
| 4 | 24 |
| M5 | Ø2 | 3 | 20 |
| 5 | 27 |
| M6 | Ø2.5 | 3 | 25 |
| 5 | 30 |
| M8 | Ø3.1 | 3 | 25 |
| 5 | 27 |
| M10 | Ø3.8 | 5 | 30 |
| 10 | 43 |
| M12 | Ø5.5 | 5 | 30 |
| 10 | 43 |
| 15 | 51 |
| M16 | Ø8 | 10 | 57 |
| 15 | 57 |
| 20 | 65 |
Back to page top
Performance info.
■Spring Load (N) of Spring Plunger (Stainless Steel)
| Load type |
Screw Dia.
(Coarse) | Nose | Ultra Light Load | Light Load | Heavy Load | Extra Heavy Load |
| Diameter | Stroke | min. | max. | min. | max. | min. | max. | min. | max. |
|
| M3 | Ø1 | 1.5 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 1.3 | 0.8 | 2.9 | 1.1 | 3.4 |
| 3 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 2.9 | 0.8 | 3.4 |
| M4 | Ø1.6 | 2 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 8.8 | 6.1 | 13.8 |
| 4 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 2.1 | 1.9 | 8.8 | 5.8 | 13.6 |
| M5 | Ø2 | 3 | 0.4 | 3.0 | 1.4 | 9.7 | 2.7 | 16.3 | 6.8 | 22.0 |
| 5 | 0.4 | 3.0 | 1.1 | 10.3 | 1.0 | 17.1 | 5.7 | 21.5 |
| M6 | Ø2.5 | 3 | 1.8 | 3.1 | 6.0 | 9.8 | 8.0 | 26.4 | 15.8 | 35.6 |
| 5 | 1.5 | 3.1 | 3.4 | 9.86 | 4.4 | 26.6 | 12.9 | 34.4 |
| M8 | Ø3.1 | 3 | 1.9 | 3.2 | 6.0 | 9.9 | 14.7 | 27.0 | 21.9 | 36.3 |
| 5 | 1.4 | 3.2 | 4.0 | 9.83 | 6.7 | 26.6 | 14.7 | 34.5 |
| M10 | Ø3.8 | 5 | 1.6 | 4.6 | 5.7 | 14.7 | 8.2 | 45.7 | 24.5 | 58.6 |
| 10 | 1.6 | 4.6 | 4.4 | 14.7 | 6.2 | 45.1 | 19.8 | 58.7 |
| M12 | Ø5.5 | 5 | 1.7 | 4.7 | 5.8 | 14.7 | 18.2 | 49.0 | 34.9 | 63.6 |
| 10 | 1.6 | 4.7 | 5.0 | 14.7 | 8.2 | 49.1 | 25.5 | 63.6 |
| 15 | 1.8 | 4.7 | 6.9 | 14.7 | 7.5 | 48.9 | 20.1 | 63.7 |
| M16 | Ø8 | 10 | 2.8 | 10.8 | 9.2 | 34.2 | 18.9 | 68.5 | 38.7 | 88.4 |
| 15 | 2.6 | 10.8 | 8.6 | 34.4 | 14.4 | 68.6 | 33.9 | 88.1 |
| 20 | 2.0 | 11.0 | 7.1 | 34.4 | 4.2 | 68.6 | 25.4 | 88.1 |
* Min. is the initial load, and max. is the load when the nose is fully compressed.
Back to page top
Adjusting Stopper Screws
| Product name | Adjusting Stopper Screws/Hexagon Socket/L Configurable/Fine Thread |
| Part number | ANBNS4-25 |
* Orange colored cells in the table below indicate the part numbers used in this example.
Selection criteria
Effective in that existing product can be used as the pin for determining the reference position.
Available sizes
■Adjusting Pin (Wit hex socket)
| Adjustment Screw | Material | Hardness | Surface Treatment |
| Fine Thread | EN 1.1191 Equiv. | 45 - 50HRC | Electroless Nickel Plating |
| Trivalent Chromate |
| EN 1.7220 Equiv. | 50HRC - |
| EN 1.4301 Equiv. | - | - |
| EN 1.4031 Equiv. | 45HRC - | - |
| Coarse Thread | EN 1.1191 Equiv. | 45 - 50HRC | Electroless Nickel Plating |
| Trivalent Chromate |
| EN 1.7220 Equiv. | 50HRC - |
| EN 1.4301 Equiv. | - | - |
| EN 1.4031 Equiv. | 45HRC - | - |
Sizes and Dimensions
| Screw Shaft Dia. (mm) | Length (mm) |
| 3 | 10 - 40 (Increments of 5) |
| 4 | 10 - 50 (Increments of 5), 60 |
| 5 | 10 - 50 (Increments of 5), 60 |
| 6 | 15 - 50 (Increments of 5), 60 |
Back to page top
IDEA NOTE Position setting before insertion of workpiece
Due to the arrangement of the spring plungers and mounting screws at both ends of each liner guide, adjustment of chuck position to center before insertion of workpiece is facilitated.