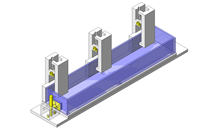
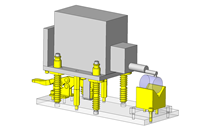
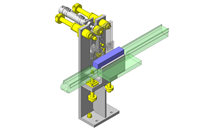
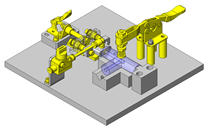
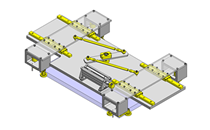
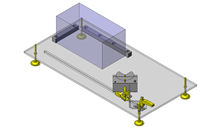
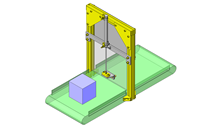
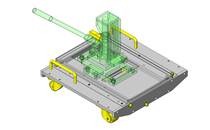
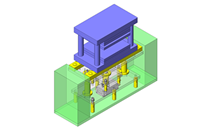
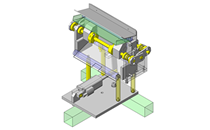
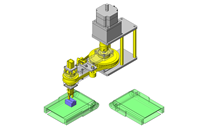
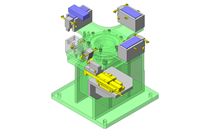
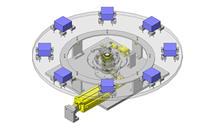
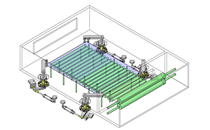
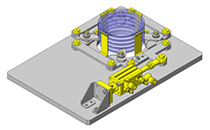
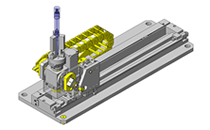
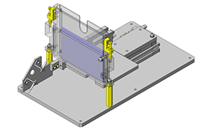
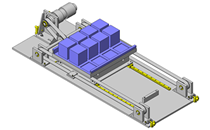
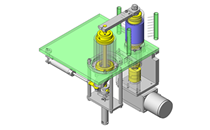
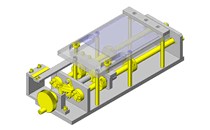
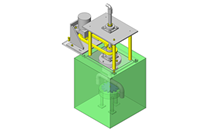
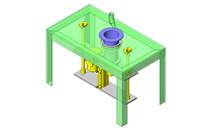
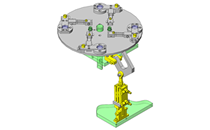
Cantilever Shafts
* Orange colored cells in the table below indicate the part numbers used in this example.
Selection criteria
Select the standard item to use as the fulcrum of the link rotation
Back to page top
Available sizes
■Cantilever Shafts - Pilot Type - Standard, Threaded, with Tapped End
| Material | Surface Treatment |
| EN 1.1191 Equiv. | Black Oxide |
| Electroless Nickel Plating |
| EN 1.4301 Equiv. | - |
■Sizes and Dimensions
Pin Dia.
(mm) | (1 mm Increments) | M(Coarse) |
| Y | F | G | N |
| 6 | 2-60 | 5-100 | 5-10 | 6-12 | M6 |
| 8 | 8-16 | M8 |
| 10 | 10-20 | M10 |
| 12 | 10-150 | 5-15 | 12-24 | M12 |
| 13 |
| 15 |
| 16 |
| 17 | 5-20 |
| 18 |
| 20 | 4-75 | 20-40 | M20 |
| M16 |
| 22 | M20 |
| M16 |
| 25 | M20 |
| M16 |
| 30 | M20 |
| M16 |
Back to page top
Accuracy Info
■Accuracy of Cantilever Shafts
Perpendicularity: 0.02
Pin Dia.
(mm) | Tolerance g6
(mm) |
|
| 6 | -0.004
-0.012 |
| 8 | -0.005
-0.014 |
| 10 |
| 12 | -0.006
-0.017 |
| 13 |
| 15 |
| 16 |
| 17 |
| 18 |
| 20 | -0.007
-0.020 |
| 22 |
| 25 |
| 30 |
Back to page top
Miniature Linear Guide
| Product name | Miniature Linear Guides/Short Block |
| Part number | SSEBSZ13L-70 |
| Features | 20% more compact than standard blocks. |
* Orange colored cells in the table below indicate the part numbers used in this example.
Selection criteria
Select a linear guide to obtain the accurate motion of claws.
Back to page top
Available sizes
■Miniature Linear Guide - Short Block
| Material | Hardness |
| Stainless Steel | 56 HRC or more |
| Free Cutting Steel (Alloy Steel including SCM) | 58 HRC or More |
■Sizes and Dimensions
| Overall Height | Block Width | Block Length | Rail Length |
|
| 8 | 17 | 19.6 | 40 ~ 130 |
| 10 | 20 | 22.9 | 35 ~ 275 |
| 13 | 27 | 27 | 45 ~ 470 |
| 16 | 32 | 32.7 | 70 ~ 670 |
Back to page top
Selection steps
■Miniature Linear Guide Selection Steps
- Determine conditions of use
- (Moving mass, feed rate, motion pattern, life)
↓
- Temporary select linear guide specifications
- (Block type, overall height, rail length are temporarily selected
according to the conditions of use.)
↓
- Basic safety check
-
- ●Allowable Load
- ●Operating Life
- ●Preload
Back to page top
Accuracy Info
■Preload and Accuracy Standards (Normal Preload, Slight Clearance type)
Light Preload, Slight Clearance Type
| Light Preload
High Grade | Slight Clearance
Standard Grade |
|
| Radial Clearance | -3 ~ 0 | 0 ~ +15 |
| Dimensional Accuracy(μm) | High Grade | Standard Grade |
| H Dimension Tolerance | ±20 | ±20 |
| Pair Variation of H | 15 | 40 |
| W2 Dimension Tolerance | ±25 | ±25 |
| Pair Variation of H | 20 | 40 |
■Running Parallelism
(μm)
| Rail Length(mm) |
| ~ 50 | 51 ~ 80 | 81 ~ 125 | 126 ~ 200 | 201 ~ 250 | 251 ~ 315 | 316 ~ 400 | 401 ~ 500 | 501 ~ 630 | 631 ~ 800 |
| High Grade | 3 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 11 | 12 | 13.5 | 14 |
| Standard Grade | 13 | 13 | 15 | 15 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 19 | 21 | 21.5 |
* The slight clearance type has clearances (play) between the rails and blocks.
Back to page top
Performance info.
■Load Rating of Miniature Linear Guides (Short Blocks, Light Preload / Slight Clearance Type)
| Overall Height | Basic Load Rating | Allowable Static Moment |
| C (Dynamic) kN | Co (Static) kN | MA
N ・ m | MB
N ・ m | Mc
N ・ m |
| 8 | 0.79 | 1.27 | 1.9 | 1.6 | 4.6 |
| 10 | 1.16 | 1.68 | 3.1 | 2.6 | 7.9 |
| 13 | 1.63 | 2.38 | 5.2 | 4.4 | 14.8 |
| 16 | 3.08 | 4.23 | 12.3 | 10.3 | 32.6 |
Back to page top
Technical calculations
■Operating Life Calculation for Linear Guides
- ●Operating Life
- When the linear guide is loaded in linear reciprocating motion, scaly damages called flaking appear due to material fatigue as the stress works on the rolling elements (steel balls) and the rolling contact surfaces (rails) constantly. Total travel distance until the first flaking occurs is called the life of linear guides.
- ●Rated Life
- Rated life is the total travel distance that 90% of linear guides of the same type can reach, under the same conditions, with no occurrence of flaking damage. Rated life can be calculated with the basic dynamic load rating and the actual load applied on the linear guides, as shown below.
-

- Load must be calculated before actually using linear guides. To obtain loads during linear reciprocating motion, it is necessary to fully consider vibrations and impacts during motion as well as distribution condition of the load applied to linear guides. So, it is not easy to calculation the loads. Operating temperature also critically affects the life. Considering these conditions, the above-mentioned calculation formula will be as follows.
-

- L: Rated Life (Km)
- fH: Hardness Factor (See Fig.1)
- fT: Temperature Factor (See Fig.2)
- fC: Contact Factor (See Table-1)
- fW: Load Factor (See Table-2)
- C: Basic Dynamic Load Rating (N)
- P: Applied Load (N)
- ●Hardness Factor (fH)
-

For linear applications, the shafts and ball bearings must have sufficient hardness. If they do not, the load rating decreases and the life will be reduced.
Please correct the rated life with the hardness factor.
- ●Temperature Factor (fT)
-

When the temperature of the linear system exceeds 100 degrees C, the hardness will decrease and as a result, the allowable load and life will reduced.
* Please use Linear Guides at within the heat resistance temperature ranges shown on product pages.
- ●Contact Factor (fC)
-
Table-1. Contact Factor
Number of Blocks per Rail Contact Factor fC
| 1 | 1.00 |
| 2 | 0.81 |
| 3 | 0.72 |
| 4 | 0.66 |
| 5 | 0.61 |
For actual applications, more than two blocks are generally used per shaft. In this case, the load applied to each block varies depending on machining precision and is not uniformly distributed. As a result, per-linear guide allowable load varies depending on the number of linear guides per rail.
Please compensate rated life with Contact Factors on Table - 1.
- ●Load Factor (fW)
-
Table-2. Load Factor
| Condition of Use | fw |
No external shocks / vibrations,
low speed 15 m/min or less | 1.0-1.5 |
No significant shocks / vibrations,
medium speed 60 m/min or less | 1.5-20 |
With external shocks / vibrations,
high speed exceeding 60 m/min | 2.0-3.5 |
To calculate load applied to the Linear Guides, in addition to object weight, it requires inertia force attributed to motion velocity or moment loads. However, it is difficult to calculation the load accurately due to potential vibrations and shocks caused by other element than repeated start-stop motions during reciprocating motion.
Thus, table-2 load factor helps simplify the life calculation.
- ●Applied Load P Calculation Method
- When moment load is applied to each block, convert the moment load into applied load by the following formula.
-

- P: Applied Load (N)
- F: Downward load (N)
- Co: Static Load Rating (N)
- MA: Allowable Static Moment - Pitching Direction (N・m)
- MC: Allowable Static Moment - Rolling Direction (N・m)
- Lp: Load Point Distance (m) in Pitching Direction
- Lr: Load Point Distance (m) in Rolling Direction
Back to page top
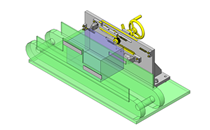
Air Linear Guides
| Product name | Air Linear Guides/MPPU10 Series |
| Part number | MPPU10-30-SMT |
* Orange colored cells in the table below indicate the part numbers used in this example.
Selection criteria
Select a drive source with guides to omit the linear motion guide of one side.
Back to page top
Available sizes
■Air Linear Guides - MPPU10 Series
| Cyl. Bore | Horizontal
(mm) | Vertical
(mm) | Thickness
(mm) | Stroke Length
(mm) |
|
| Ø10 | 27 | 70 | 20 | 15 |
| 85 | 30 |
| 100 | 45 |
| Ø12 | 32 | 76 | 22 | 20 |
| 86 | 30 |
| 101 | 45 |
| 116 | 60 |
Back to page top
Accuracy Info
| Bore Dia. | Ø10 | Ø12 |
| Stroke | 15/30/45 | 20/30/45 | 60 |
| Parallelism | Plane C to Plane A | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Plane D to Plane B | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Running Parallelism | Plane C to Plane A | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.006 |
| Plane D to Plane B | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.006 |
| Perpendicularity | Plane E to Plane A | 0.15 | 0.15 |
| Plane E to Plane B | 0.15 | 0.15 |
| J Dimension Tolerance | ±0.025 | ±0.025 |
| F Dimension Tolerance | ±0.2 | ±0.2 |
| G Dimension Tolerance | ±0.2 | ±0.2 |
| H Dimension Tolerance | ±0.05 | ±0.05 |
Back to page top
Performance info.
■Speeds / Loads (Load Info.) of Air Linear Guides
■Operating Pressure Range
Min. Operating Pressure (MPa): 0.15
Max. Operating Pressure (MPa): 0.70
Pressure Resistance (Mpa): 1.05
■Theoretical Thrust
Unit: N
Cyl.
Bore | Operation
Direction | Rod Dia.
(mm) | Operating Pressure (MPa) |
| 0.4 | 0.5 |
| Ø10 | Outstroke | Ø4 | 31 | 39 |
| Instroke | 26 | 33 |
| Ø12 | Outstroke | Ø5 | 45 | 57 |
| Instroke | 37 | 47 |
■Basic Static Load Ratings / Allowable Static Moments
Cyl.
Bore | Stroke
(mm) | Basic Static
Load Rating Co(kN) | Allowable Load Moment N・m |
| Pitching | Yawing | Rolling |
| Ø10 | 15/30/45 | 3.4 | 20.5 | 24.5 | 22.5 |
| Ø12 | 20/30/45/60 | 4.9 | 32.3 | 38.2 | 41.1 |
Back to page top
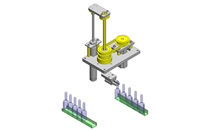
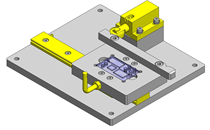
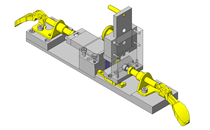
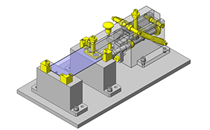
IDEA NOTE Centering method
The push and pull of the cylinder moves the linear guide and the claw. The motion is transferred to another claw through the fulcrum to make both the right and left claws center evenly.